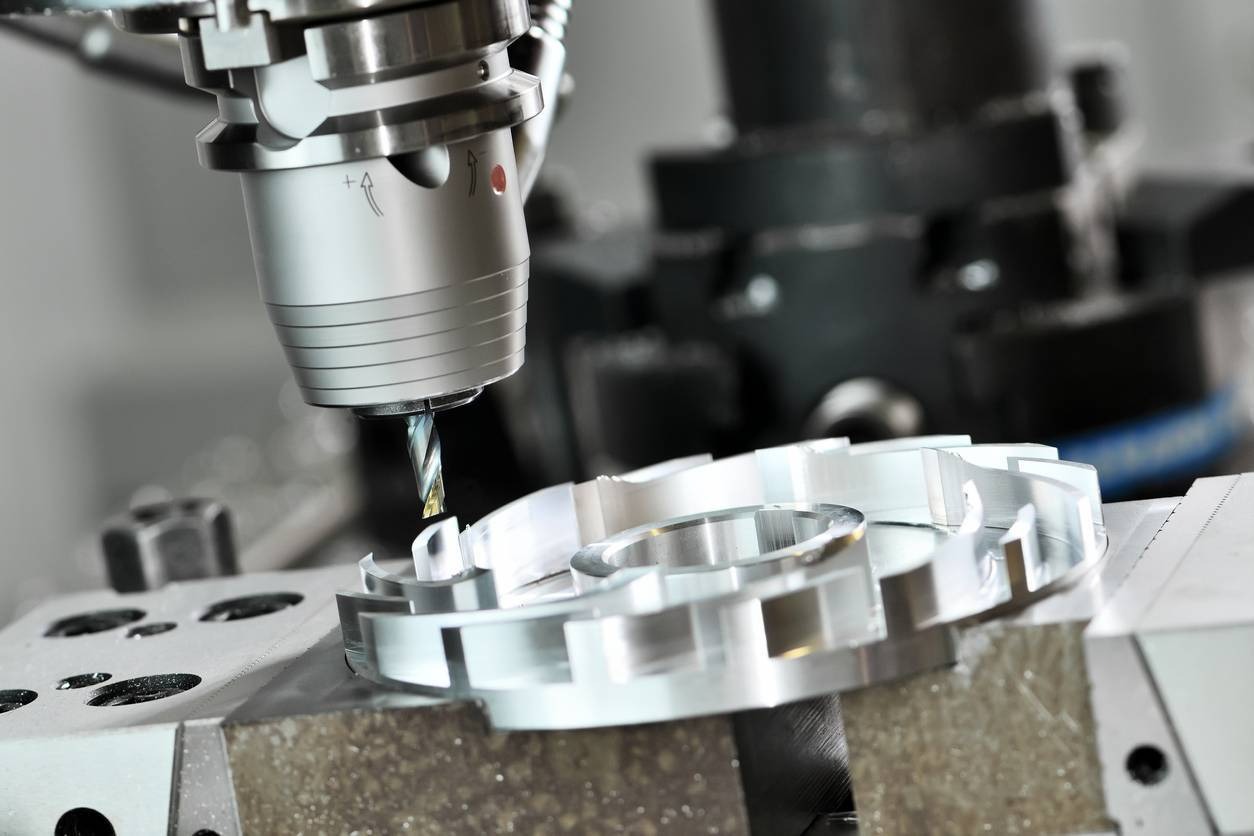
Introduction
In modern manufacturing, efficiency and precision are key determinants of competitiveness. Among the many types of CNC equipment, the Horizontal Machining Center (HMC) has become one of the most widely adopted solutions across industries. Unlike a vertical machining center (VMC), an HMC features a horizontally oriented spindle, which provides superior chip evacuation, enhanced stability, and the ability to machine multiple surfaces of a workpiece in a single setup.
These capabilities make HMCs particularly valuable for industries that demand high productivity, consistent accuracy, and cost efficiency. From mass-production environments such as automotive factories to high-precision sectors like aerospace and medical equipment, HMCs are transforming how manufacturers produce complex parts at scale.
This article examines the key industries that rely on horizontal machining centers, highlighting why they prefer HMCs over other machining solutions, the unique challenges these industries encounter, and how HMC technology facilitates their long-term growth.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is one of the largest users of horizontal machining centers, driven by its constant demand for high-volume production and uncompromising precision. Components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, brake system parts, steering knuckles, and axle components require complex machining on multiple surfaces. Achieving this level of detail with consistency is a challenge for traditional setups, but HMCs are uniquely designed to meet these needs.

Key Challenges in Automotive Manufacturing
High-volume production: Automakers must produce thousands of identical components within short cycle times.
Tight tolerances: Safety-critical parts, such as engine or brake components, require micron-level precision.
Complex geometries: Many automotive parts involve intricate internal and external features.
Cost pressure: With fierce market competition, manufacturers seek machines that reduce production costs while maintaining quality.
Why HMCs Excel in the Automotive Industry
Continuous operation: Most HMCs are equipped with pallet changers, allowing one part to be machined while another is being loaded, significantly reducing downtime.
Multi-face machining: An HMC can process multiple sides of a component in a single setup, improving accuracy and cutting setup time.
Efficient chip removal: The horizontal spindle orientation ensures better chip evacuation, essential when machining deep cavities in engine blocks or housings.
Scalability: From small-batch prototyping to mass production, HMCs adapt easily to changing production requirements.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry places some of the highest demands on machining technology due to its reliance on lightweight yet extremely durable materials and its strict compliance with safety standards. Every component, from turbine blades to landing gear parts, must meet micron-level tolerances and withstand extreme operating conditions. For this reason, horizontal machining centers (HMCs) have become a vital asset for aerospace manufacturers.
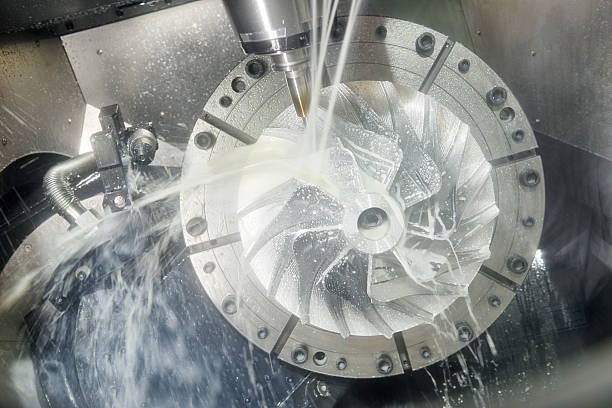

Key Challenges in Aerospace Manufacturing
Difficult-to-machine materials: Aerospace components are often made of titanium, Inconel, and other superalloys that are extremely hard and cause rapid tool wear.
Complex geometries: Structural parts, turbine components, and aerospace fasteners require multi-surface machining with intricate details.
Low-volume, high-value production: Unlike the automotive industry, aerospace often produces fewer units, but each part is highly valuable and time-intensive to manufacture.
Strict certification standards: Components must meet rigorous regulatory requirements for safety and performance.
Why HMCs Are Essential for Aerospace
Rigidity and power: HMCs provide the spindle strength and structural stability needed for heavy-duty machining of exotic alloys.
Multi-axis capabilities: 4- and 5-axis horizontal machining centers enable precise machining of complex aerospace parts like turbine blades and impellers in a single setup.
Superior chip evacuation: Horizontal spindle orientation ensures effective chip removal, preventing tool damage and part inaccuracies when cutting deep pockets.
Consistency and accuracy: HMCs maintain tight tolerances over long machining cycles, which is critical for aerospace safety standards.
Mold & Die Industry
The mold and die industry is highly demanding when it comes to precision, surface finish, and machining complexity. Manufacturers produce components for injection molding, stamping, and die-casting, which require high dimensional accuracy and flawless surface quality. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) have become essential in this sector due to their ability to handle large workpieces, deep cavities, and complex geometries efficiently.
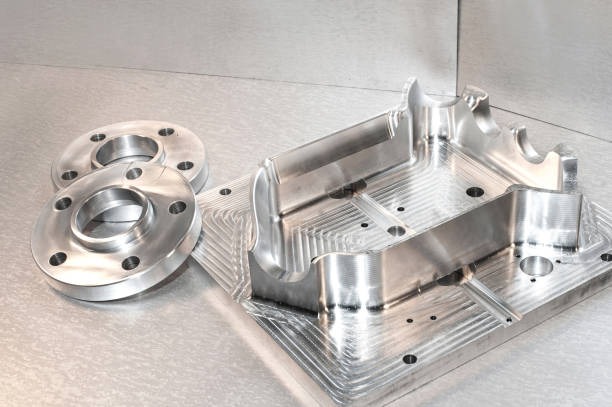

Key Challenges in Mold & Die Manufacturing
Complex surfaces: Molds often have intricate cavities and multi-surface features that are difficult to machine with traditional methods.
Heavy and large workpieces: Some molds weigh several tons, requiring machines with high rigidity and stability.
Long machining cycles: Achieving high precision over extended machining periods is critical to prevent dimensional drift.
Surface quality requirements: Mold components must have smooth finishes to ensure the quality of the final product.
Why HMCs Excel in Mold & Die Applications
Large table sizes and high rigidity: HMCs can accommodate heavy mold blocks and maintain precision during deep cuts.
Multi-face machining: A single setup can machine multiple surfaces, reducing setup time and errors.
Efficient chip evacuation: Horizontal spindles remove chips effectively, minimizing tool wear and preventing surface imperfections.
Automation-ready: Pallet changers and robotic integration allow continuous operation for higher throughput.
Heavy Machinery & Construction Equipment
Manufacturers of heavy machinery and construction equipment face unique challenges due to the size, weight, and strength requirements of their components. From excavator frames to large gearboxes, these parts demand machines that can handle heavy-duty cutting, maintain precision, and operate reliably under high loads. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) have become a preferred solution for this industry.
Key Challenges in Heavy Machinery Manufacturing
Large and heavy components: Parts like chassis, hydraulic housings, and mining equipment frames are oversized and require machines with large work envelopes and high rigidity.
High-strength materials: Components are often made from alloy steels or cast iron, requiring robust cutting power.
Extended machining cycles: Long production runs can strain machines, making reliability and stability critical.
Tight tolerances: Despite the size, precise dimensions are required for assembly and performance.
Why HMCs Are Ideal for Heavy Machinery
High torque and spindle power: HMCs can cut through tough materials efficiently without sacrificing accuracy.
Large, stable tables: They provide support for oversized and heavy workpieces while maintaining precision.
Multi-face machining: Reduces setups by allowing multiple sides of a part to be machined in a single operation.
Automation compatibility: Integration with pallet systems or robotic arms allows continuous operation, minimizing downtime for large-batch production.
Energy & Power Generation
The energy and power generation sector relies heavily on precision, durability, and reliability in machining critical components such as turbine casings, generator housings, and wind turbine hubs. Components must withstand high mechanical loads, extreme temperatures, and long operational life, making horizontal machining centers (HMCs) a preferred choice for manufacturers in this industry.
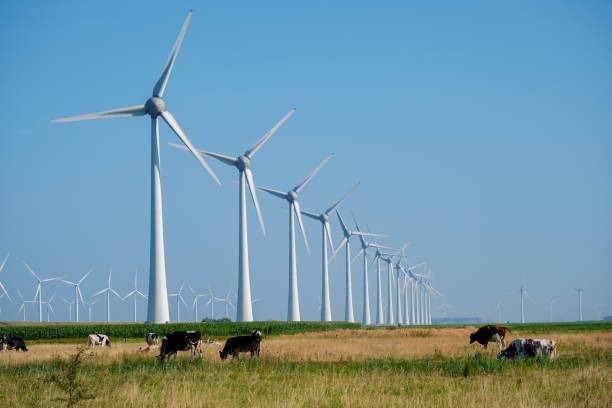

Key Challenges in Energy Manufacturing
Large and complex components: Turbine and generator parts are often oversized, with intricate internal and external geometries.
High material hardness: Many components are made from cast iron, steel alloys, or specialized composites.
Critical dimensional accuracy: Parts must meet strict tolerances to ensure proper assembly and safe operation.
Long production cycles: Extended machining hours require stable and reliable machines.
Why HMCs Are Ideal for Energy Applications
Large work envelope and table capacity: HMCs can accommodate oversized turbine components without compromising accuracy.
Enhanced rigidity and stability: Ensures dimensional consistency during heavy cutting of large, dense materials.
Multi-face machining capabilities: Multiple surfaces can be machined in a single setup, reducing setup times and errors.
Efficient chip evacuation: Horizontal spindle orientation improves chip removal for deep cavities, protecting tooling and surface quality.
Automation-ready: Pallet changers and robotic integration enable continuous operation for high-volume or heavy-duty components.
Medical Equipment & Precision Components
The medical and precision equipment sector demands exceptional accuracy, surface finish, and reliability due to the critical nature of its components. From orthopedic implants to imaging devices and surgical instruments, parts must meet tight tolerances and comply with strict regulatory standards. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) are increasingly used in this sector because they offer precision, efficiency, and adaptability for small-batch, high-value production.
Key Challenges in Medical Manufacturing
High precision requirements: Components often require tolerances in the range of microns.
Small batch, high-mix production: Unlike mass industries, medical manufacturers produce low-volume but highly complex parts.
Diverse materials, including titanium, stainless steel, and specialized alloys, require careful machining to prevent deformation or damage.
Regulatory compliance: Parts must meet ISO and FDA standards, leaving little room for error.
Why HMCs Are Ideal for Medical Equipment
Multi-axis machining: 4- and 5-axis HMCs enable the machining of complex geometries in a single setup, thereby improving accuracy and consistency.
High repeatability: HMCs maintain tight tolerances even during extended runs, essential for implant and device components.
Efficient chip evacuation: Prevents surface defects when machining deep cavities or small features.
Automation and flexibility: Pallet changers and robotic integration enable small-batch production without sacrificing efficiency.
Electronics & Telecommunications
The electronics and telecommunications industry requires high precision, fast production cycles, and flexibility due to the rapid evolution of technology and product designs. Components such as device housings, heat sinks, and communication equipment frames demand accurate machining and excellent surface finish, often in medium-batch production. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) are increasingly chosen for this sector due to their precision, speed, and adaptability.
Key Challenges in Electronics & Telecommunications
Thin-wall and delicate components: Many parts are lightweight but require rigid machining to prevent deformation.
Fast product cycles: Electronics demand rapid adaptation to new models, requiring quick setup changes.
High thermal conductivity materials: Aluminum and copper alloys are commonly used, requiring effective chip evacuation.
Medium-batch variety: Manufacturers often produce multiple versions or iterations in small to medium quantities.
Why HMCs Are Ideal for This Industry
High spindle speed and precision: Ensures accurate machining of delicate and thin-walled parts.
Efficient chip evacuation: Horizontal spindle orientation helps prevent surface damage when cutting aluminum or copper components.
Quick changeovers: Pallet changers and automated systems reduce downtime for multiple batch production.
Multi-face machining: Components can be machined on multiple surfaces in a single setup, improving consistency.
Cross-Industry Benefits of Horizontal Machining Centers
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) have proven their value across a wide range of industries—from automotive and aerospace to medical equipment, energy, and telecommunications. Despite the differences in applications, there are several core benefits that make HMCs the preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide.
Exceptional Efficiency
Continuous operation: Pallet changers allow one part to be machined while another is loaded or unloaded, minimizing downtime.
Multi-face machining: Complex parts can be machined on multiple surfaces in a single setup, reducing total cycle time.
High throughput: Ideal for mass production environments such as automotive and heavy machinery manufacturing.
Superior Precision and Accuracy
Tight tolerances: HMCs maintain micron-level accuracy even over long production cycles, essential for aerospace, medical, and energy applications.
Consistent quality: Multi-axis machining ensures uniformity across batches, minimizing errors and reducing scrap.
Stable machining: Horizontal spindle orientation reduces vibration, improving surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Versatility and Adaptability
Wide range of materials: HMCs can machine aluminum, steel, titanium, copper, and other alloys efficiently.
Multi-industry applications: From large, heavy-duty parts to small, precision components, HMCs adapt to diverse manufacturing needs.
Flexible production: Suitable for low-volume prototypes, medium-batch runs, or high-volume mass production.
Automation-Ready for Smart Manufacturing
Integration with robotics: Robotic arms can automate loading and unloading, improving safety and efficiency.
Pallet pool systems: Enable unattended machining, especially beneficial in 24/7 operations.
Industry 4.0 compatibility: IoT sensors and real-time monitoring allow predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
Cost-Effectiveness
Reduced labor and setup costs: Fewer setups and multi-face machining save time and manpower.
Extended tool life: Efficient chip evacuation and stable machining reduce wear on cutting tools.
Higher ROI: Faster cycle times, less scrap, and consistent part quality increase overall profitability.
Conclusion
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) have proven themselves as versatile, high-precision, and efficient solutions across a wide range of industries—from automotive and aerospace to medical equipment, energy, and electronics. By addressing the unique challenges of each sector, HMCs enable manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances, faster production cycles, and consistent quality, whether machining large, heavy-duty components or intricate, high-precision parts.
The adoption of HMCs is further accelerated by automation, multi-axis capabilities, and Industry 4.0 integration, making them a key driver of modern manufacturing efficiency and competitiveness. With the ability to handle diverse materials, complex geometries, and both low- and high-volume production, HMCs offer unmatched versatility for today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
If your industry requires reliable, high-performance horizontal machining solutions, now is the time to explore how HMCs can transform your production capabilities. At CNC Yangsen, we provide cost-effective, high-quality HMCs tailored to meet the demands of your specific applications.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover the ideal Horizontal Machining Center for your business.